Unveiling the Token Economy of the Leading Oracle Network
A Comprehensive Analysis of Chainlink's Tokenomics
Introduction
One crucial factor contributing to the security of blockchains is their closed ecosystem, which relies solely on the data generated within their network, known as on-chain data. However, this inherent characteristic poses limitations on blockchain technology, preventing it from working seamlessly with external data sources, commonly referred to as off-chain data. This is where Oracle Services come into play, and among them, Chainlink stands out as the most established Oracle Network, supporting nearly 2000 dApps across 15 different blockchains and layer-2 solutions.
Chainlink's primary mission centres around solving the "oracle problem," which arises from the inability of blockchains to natively interact with external off-chain systems due to the strong security properties imposed by their consensus mechanism. By bridging the gap between on-chain and off-chain data, Chainlink enables decentralized applications (dApps) to access reliable real-world data securely.
In this Tokenomics 101 analysis, a foundational understanding of the participants within an oracle network will be provided, and how they interact with Chainlink's native token, $LINK. The fundamental dynamics of Chainlink's tokenomics will be explored, as well as its role in incentivizing various ecosystem participants, contributing to the network's security, reliability, and growth.
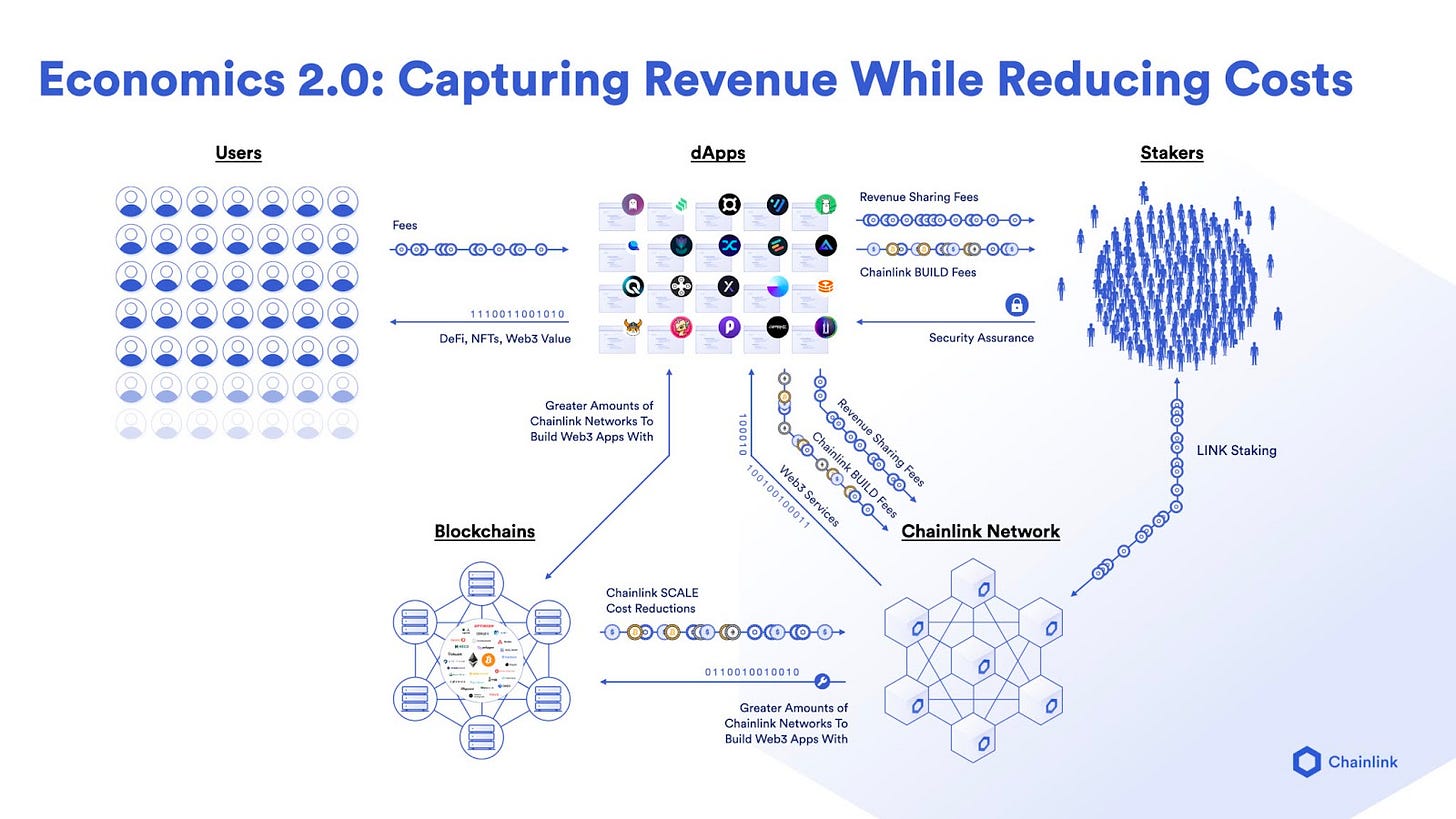
$LINK Tokenomics
(A zoomable version of the diagram can be found here)
Ecosystem Participants
Oracle Nodes
Oracle Nodes play a crucial role in the Chainlink network, serving as intermediaries between (off-chain) data sources and smart contracts of dApps. These nodes are responsible for converting the necessary off-chain data into a format that smart contracts can understand and process, enabling the integration of external data within the blockchain environment.
Each Oracle Node stakes a certain amount of $LINK tokens as collateral, guaranteeing reliable, honest, and high-quality performance. By doing so, they earn staking rewards and fees from dApps and/or blockchains.
Alerters
Alerters are stakeholders who actively monitor the performance of node operators. Their primary objective is to ensure that node operators fulfil their obligations as agreed upon within the network. Alerters diligently observe the operations of node operators and promptly raise alerts if they detect any discrepancies or failures in their performance. By alerting in a timely and accurate manner, Alerters contribute to maintaining the integrity and reliability of the Chainlink network. In recognition of their role, Alerters have the opportunity to receive rewards for their monitoring and active participation in upholding the network's standards.
Oracle Nodes can also act as Alerters, continuously monitoring their fellow Node-Peers. These nodes possess a 20-minute priority time, giving them the advantage of raising an alert before other Alerters can do so.
Data Providers
Data Providers contribute their data to the network. There are two methods through which data providers can participate in the Chainlink network:
Simple: Standard API Model
Data providers have the option to monetize their data by offering access to it through their already existing APIs. In this scenario, Chainlink nodes interact with the data provider's API to retrieve the required data. The data provider can seamlessly integrate with Chainlink, leveraging the network's capabilities to monetize their data without significant changes to their existing business model.
Advanced: Origin Signed Data
Alternatively, data providers also have the opportunity to directly bring their data on-chain. In this case, they become their own node within the Chainlink network, eliminating the need for other Chainlink nodes as intermediaries. By bringing their data on-chain, data providers can enhance the efficiency and reliability of data delivery, while maintaining control over the entire data provision process.
Data Recipient
Data Recipients, essentially dApps within the ecosystem, play a crucial role as they rely on the provided data while aiming to avoid centralized data delivery infrastructure and services. These recipients seek decentralized oracle solutions, such as Chainlink, to access reliable and verified data, enabling them to maintain the trustless and transparent nature of blockchain applications. By leveraging decentralized data sources, these dApps can uphold the core principles of decentralization and enhance the security and reliability of their smart contract operations.
Protocol Components
In this section, two innovative programs launched by Chainlink will be introduced. The programs are designed to facilitate the broader adoption of decentralized oracle solutions and drive the growth of the Chainlink ecosystem.
Chainlink SCALE
The SCALE program, short for "Sustainable Chainlink Access for Layer 1 and 2 Enablement," empowers blockchains and layer-2 networks to accelerate smart contract innovation within their native ecosystems. In this program, the respective blockchains and layer-2 networks cover the operating costs, including transaction gas fees, of Chainlink oracle networks for a specified time period. As a result, these projects gain access to enhanced features and vital oracle services specifically tailored to meet their ecosystem needs. This may include configurations like Data Feeds with higher update frequencies, enabling the development of more sophisticated and low-latency smart contract applications. By facilitating the integration of Chainlink's reliable oracle solutions without financial barriers, the SCALE program effectively supports developers and projects, enabling them to leverage advanced oracle services and drive the growth of decentralized applications within their ecosystems.
Learn more about the Chainlink SCALE program here.
Chainlink BUILD
Chainlink BUILD is an instrumental program aimed at fostering the growth and advancement of both early-stage and established projects within the Chainlink ecosystem. Through BUILD, participants gain enhanced access to Chainlink services and receive comprehensive technical support. In exchange for these valuable resources, projects commit a portion of their network fees and offer other incentives to the program, such as dedicating a percentage of their total token supply to BUILD. This commitment strengthens the overall network and facilitates the development of dApps that leverage Chainlink's decentralized oracle solutions.
Learn more about the Chainlink BUILD program here.
These programs demonstrate Chainlink's dedication to supporting blockchain projects and nurturing the thriving ecosystem of decentralized applications. By offering sustainable access and fostering collaboration, Chainlink actively empowers developers and projects to leverage the power of secure and reliable external data in their smart contracts, leading to greater adoption and advancement of blockchain technology on a global scale.
Value Creation
The problem that Chainlink is addressing revolves around the critical issue of accessing reliable, real-world data within blockchain networks. Blockchains, by design, operate in a closed and isolated environment, making it challenging to interact with external data sources directly. However, many smart contract applications and decentralized platforms heavily rely on trustworthy data to execute automated actions. This creates a fundamental dilemma known as the "Oracle problem". Oracles act as bridges between the blockchain and the outside world, providing access to external data for smart contracts to process. However, integrating oracles into decentralized applications raises concerns about centralization, security, and data integrity. Traditional centralized oracles may pose a single point of failure and could be susceptible to manipulation, compromising the entire decentralized nature of blockchain systems. Hence, finding a robust, decentralized, and tamper-proof solution to the oracle problem is crucial for the widespread adoption and seamless functionality of smart contracts within the blockchain ecosystem. This is precisely the challenge that Chainlink seeks to solve through its innovative approach to decentralized oracle services.
Overall Goal
Chainlink effectively addresses the critical problem of connecting blockchain networks with external data resources through its decentralized oracle network. By harnessing a vast and diverse network of independent Oracle node operators, Chainlink provides a comprehensive solution to the Oracle problem. Through this network, smart contracts gain access to a wide range of decentralized services, enabling them to securely and efficiently interact with real-world data.
Chainlink's Price Feeds offer essential financial market data, powering various DeFi applications with reliable information. Verifiable randomness ensures the creation of dynamic NFTs and enables fair on-chain gaming applications. The provision of proof of reserve assures users of the backing collateral supporting stablecoins and cross-chain tokens. Additionally, the Keeper Network introduces transaction automation bots, offering autonomous DevOps services. Chainlink's decentralized oracle network not only ensures data integrity and transparency but also mitigates the risks associated with centralization, such as single points of failure and data manipulation. By bridging the gap between blockchain and external data sources, Chainlink plays a pivotal role in unlocking the full potential of smart contracts and decentralized applications, fostering innovation and adoption across the blockchain ecosystem.
(Comp. Messari)
Value Capture
Value Accrual to Protocol
The protocol does not participate in value accrual. Instead, the fees and rewards are entirely earned by the Service Providers, primarily the Oracle Nodes.
Value Accrual to Token
There is no direct value accrual to $LINK. However, $LINK is used to pay for services on the Chainlink network and thus the Equation of Exchange suggests that the token price rises with increasing transactional volume, considering the total $LINK supply remains the same, as well as the average holding period of $LINK.
In one of my previous Tokenomics 101s, I covered the Streamr network where I dived deeper into the Equation of Exchange, feel free to give it a read if you are interested in this topic.
Business Model
(Please find an enlarged version of the image here)
Revenue comes from:
dApps:
Revenue Sharing
Blockchains:
Revenue is denominated in:
Primarily in $LINK
Revenue goes to:
Node Operator Stakers
Community Stakers
Token Utility
Fee Token
$LINK serves as the primary fee token within Chainlink's ecosystem. Users utilize $LINK tokens to access and acquire valuable data from the network.
Staking for Node Operations
To become a Chainlink node operator and participate in the network's decentralized oracle infrastructure, individuals must stake a certain amount of $LINK. This stake acts as collateral and ensures the integrity and reliability of its services.
Community Staking and Auto-Delegation
Apart from node operators, community members also have the opportunity to stake their $LINK tokens. These staked tokens are automatically delegated to eligible node operators, further strengthening the network's decentralization and encouraging active participation from the community.
Collateral for DeFi Loans
$LINK can be used as collateral to secure decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem loans. By pledging their $LINK tokens as collateral, individuals can access borrowing options and unlock liquidity while retaining ownership of their assets. This use case expands the utility of $LINK and enhances its role as a valuable asset within the DeFi space.
$LINK Demand Drivers
Demand for Decentralized Oracles
With the increasing demand for trustworthy and authenticated data within blockchain applications, there is a growing need for Chainlink's robust oracle solutions. This surge in demand for Chainlink's oracle services drives the corresponding need for $LINK tokens, which are utilized as a means of payment to access and utilize these reliable data services.
Integration into DeFi Ecosystem
Chainlink has become a fundamental component of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. Many DeFi protocols rely on Chainlink's oracles to access external data for functions such as price feeds, lending/borrowing rates, and more. As the popularity and adoption of DeFi projects rise, the demand for $LINK tokens increases to access and utilize Chainlink's oracle services.
Node Operation and Staking
To become a Chainlink node operator and participate in the network, individuals need to stake a certain amount of $LINK tokens. This requirement creates demand for $LINK tokens as aspiring node operators acquire them to fulfil the staking criteria and take part in the network's decentralized oracle infrastructure.
$LINK Distribution & Unlocks
Node Operators
A significant portion of the token supply, precisely 30% (300 million $LINK), has been allocated as rewards for Node Operators and Ecosystem Incentives. This allocation serves as an incentive to encourage active participation and contribution from Node Operators, who play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the Chainlink network.
Initial Sale
During a public sale conducted in 2017, 35% (350 million $LINK) of the token supply was sold. This initial sale provided an opportunity for early participants and supporters of the project to acquire $LINK tokens and contribute to the growth and development of the Chainlink ecosystem.
Development Team
A separate allocation of 35% (350 million $LINK) has been allocated to Chainlink's parent company, which holds responsibility for the future development of the project. This allocation ensures that the development team has the necessary resources to further enhance and expand the capabilities of the Chainlink network, driving innovation and continuous improvement.
Based on our research, Chainlinks documentation does not provide specific details about the vesting schedule associated with the respective token allocations. If any member of the Chainlink team is reading this and possesses information regarding the vesting schedule, feel free to contact us. Your assistance in providing this information would be greatly appreciated.
Circulating Supply
As of the current date (09.07.2023), the circulating supply of $LINK stands at 538,099,970.45 tokens, which represents approximately 53.81% of the maximum supply capped at 1,000,000,000 $LINK. It's worth noting that for the token price to remain around the current value of approximately $6.15, the price would need to roughly double when the maximum supply is reached. This calculation considers the relationship between the circulating supply and the total supply and emphasizes the potential impact on the token's price as the supply approaches its maximum limit.
Feedback Loops
Enhancing the security and reliability of the Chainlink network
By attracting a greater number of independent node operators to join the network, the security and reliability of the Chainlink ecosystem are significantly strengthened. This is due to the increasing improbability of a malicious node being able to carry out fraudulent actions. As the network expands and incorporates more diverse and independent nodes, the overall system becomes more robust, resistant to attacks, and capable of delivering trustworthy and tamper-proof data to smart contracts. The decentralized nature of the oracle network ensures a higher level of resilience and mitigates the risk of single points of failure or manipulation.
Increase in demand for Chainlink's oracle services due to a higher number of oracle nodes
As the number of oracle nodes within the Chainlink network increases, the demand for Chainlink's oracle services experiences a corresponding rise. This growth in the number of independent nodes contributes to a more secure and decentralized network, reducing the vulnerability to malicious attacks. By bolstering security and enhancing the network's integrity, the value of the Chainlink network increases, attracting new users who prioritize higher security standards. This increased trust and confidence in the network drive the demand for Chainlink's oracle services as more users are onboarded, further solidifying the network's position as a trusted and reliable provider of decentralized oracle solutions.
Impact of increase/decrease in the required minimum collateral on network security
The security of the Chainlink network is significantly influenced by changes in the required minimum collateral for node operators. If Chainlink decides to increase the collateral requirements, it may result in some prospective nodes failing to meet the new criteria. Consequently, these nodes would be unable to contribute to the network's security, leading to reduced decentralization. On the other hand, a decrease in the collateral requirements could attract more nodes to join the network. However, a lower capital requirement might create a potential vulnerability, as it may not provide sufficient protection against malicious attacks.
Increase in $LINK's price due to more node operators
In addition to enhancing the security and reliability of the network, the growing number of node operators contributes to an increase in the demand for $LINK tokens. Aspiring node operators are required to stake $LINK in order to participate in the network, creating an increased demand for the token. This increased demand, driven by the need to acquire and stake $LINK, can potentially lead to upward pressure on the token's price as the network attracts more participants and expands its decentralized oracle infrastructure.
Increase in $LINK's price due to higher demand for oracle services
The rising demand for decentralized oracle services directly translates to an increased demand for $LINK tokens. As more blockchain applications, such as DeFi protocols, require reliable and verified data from external sources, the demand for Chainlink's oracle services grows. This surge in demand naturally leads to an increased demand for $LINK tokens, which are used as the primary means of accessing and paying for these oracle services. As a result, an upswing in the demand for $LINK can be expected, potentially driving an increase in the token's price as the ecosystem experiences a heightened demand for its oracle services.
Observations/Thoughts
A more transparent vesting schedule
For both current $LINK token holders and potential investors, having clarity on the inflation of $LINK over the upcoming years is of utmost importance. This information can be calculated if details about the release schedule and vesting plan were available. However, during the research, no reliable information on a vesting schedule could be found. With approximately 50% of the total supply already in circulation, it becomes particularly crucial to understand how and when the remaining 50% will enter the circulating supply. Having this information would provide valuable insights into the future supply dynamics and potential impact on the token's value and overall tokenomics.
Highly Gas-Cost Intense Business
The Oracle business is notably gas-intensive. While the revenue has generally exceeded the gas costs in recent months (measured against the ETH/USD price feed), there have been instances when the gas costs significantly outweighed the revenue. Should this situation persist over an extended period, it could potentially lead to nodes departing from the Chainlink network due to unprofitability. Such an outcome may compromise the network's decentralization and security, highlighting the need for careful management of incentives and pricing to sustain the network's long-term viability and integrity.
(Zoomable and interactive chart available here)
(Zoomable and interactive chart available here)
Summary
In this comprehensive Tokenomics 101 analysis of Chainlink ($LINK), the focus was on exploring the decentralized oracle network's tokenomics and its pivotal role in tackling the challenging "oracle problem." The introduction provided a concise overview of Chainlink's mission, aiming to connect blockchain networks with external data sources and emphasizing the significance of solving the oracle problem for decentralized applications.
Throughout the analysis, a deep dive into Chainlink's token utility revealed its fundamental role as the primary medium of exchange within the ecosystem. Additionally, the importance of staking $LINK for node operations and community engagement was highlighted, elucidating how these mechanisms contribute to network security and decentralization.
The Ecosystem Participants section offered valuable insights into the integral roles played by Oracle Nodes, Data Providers, and Alerters. By ensuring the security and reliability of the Chainlink network, each participant contributes to the ecosystem's success. Moreover, the distribution of token allocation shed light on the rewards and incentives provided to Node Operators and the initial sale of $LINK tokens, illustrating the strategic planning behind the token distribution.
Two pioneering programs, SCALE and BUILD, were discussed in detail, revealing Chainlink's commitment to promoting mass adoption and fostering project growth within the ecosystem. The impact of collateral requirements on network security was explored, emphasizing the need to strike the right balance to ensure optimal security without hindering participation.
Overall, Chainlink's tokenomics exemplify a thoughtfully designed system that incentivizes participation, enhances security, and fosters seamless data integration within blockchain applications. The network's innovative programs and efforts to overcome challenges demonstrate its commitment to mass adoption and continued growth. As the blockchain industry evolves, Chainlink's decentralized oracle solutions are poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of decentralized applications, powering the ecosystem forward with its reliable and secure data solutions.